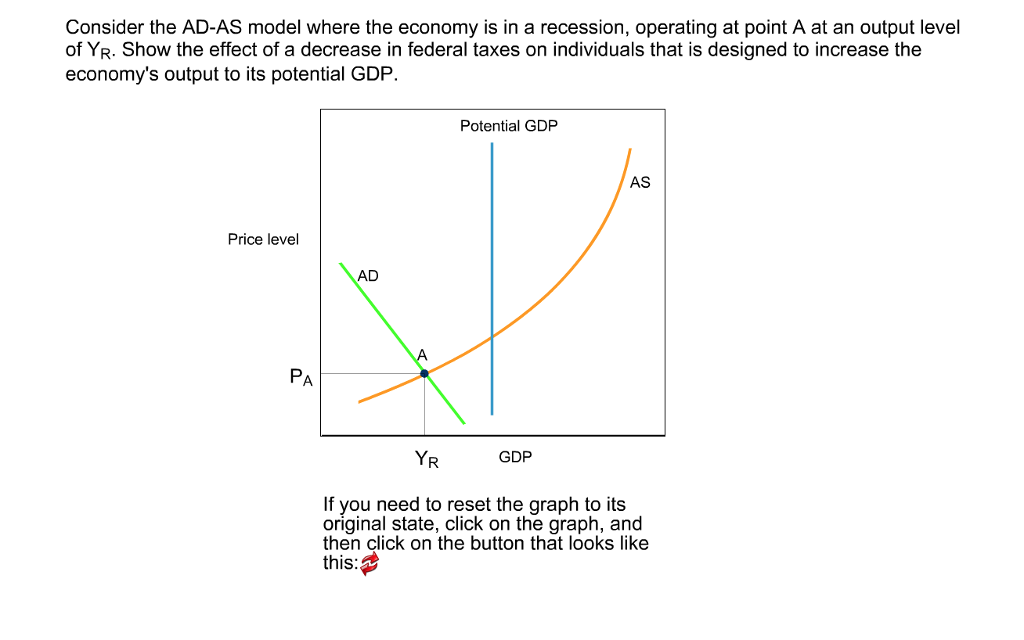
Solved Consider the ADAS model where the economy is in a
What is the equilibrium? Step 1. Draw your x- and y-axis. Label the x-axis "Real GDP" and the y-axis "Price Level." Step 2. Plot AD on your graph. Step 3. Plot AS on your graph. Step 4. Look at Figure 2, which provides a visual to aid in your analysis. Figure 2. The AS-AD Curves AD and AS curves created from the data in Table 1. Step 5.
[Solved] Assume an economy operating below full employment. Draw a
The aggregate demand/aggregate supply, or AD/AS, model can be used to illustrate both Say's Law and Keynes' Law. Say's Law states that supply creates its own demand; Keynes' Law states that demand creates its own supply. Take a look at the AD/AS diagram below.
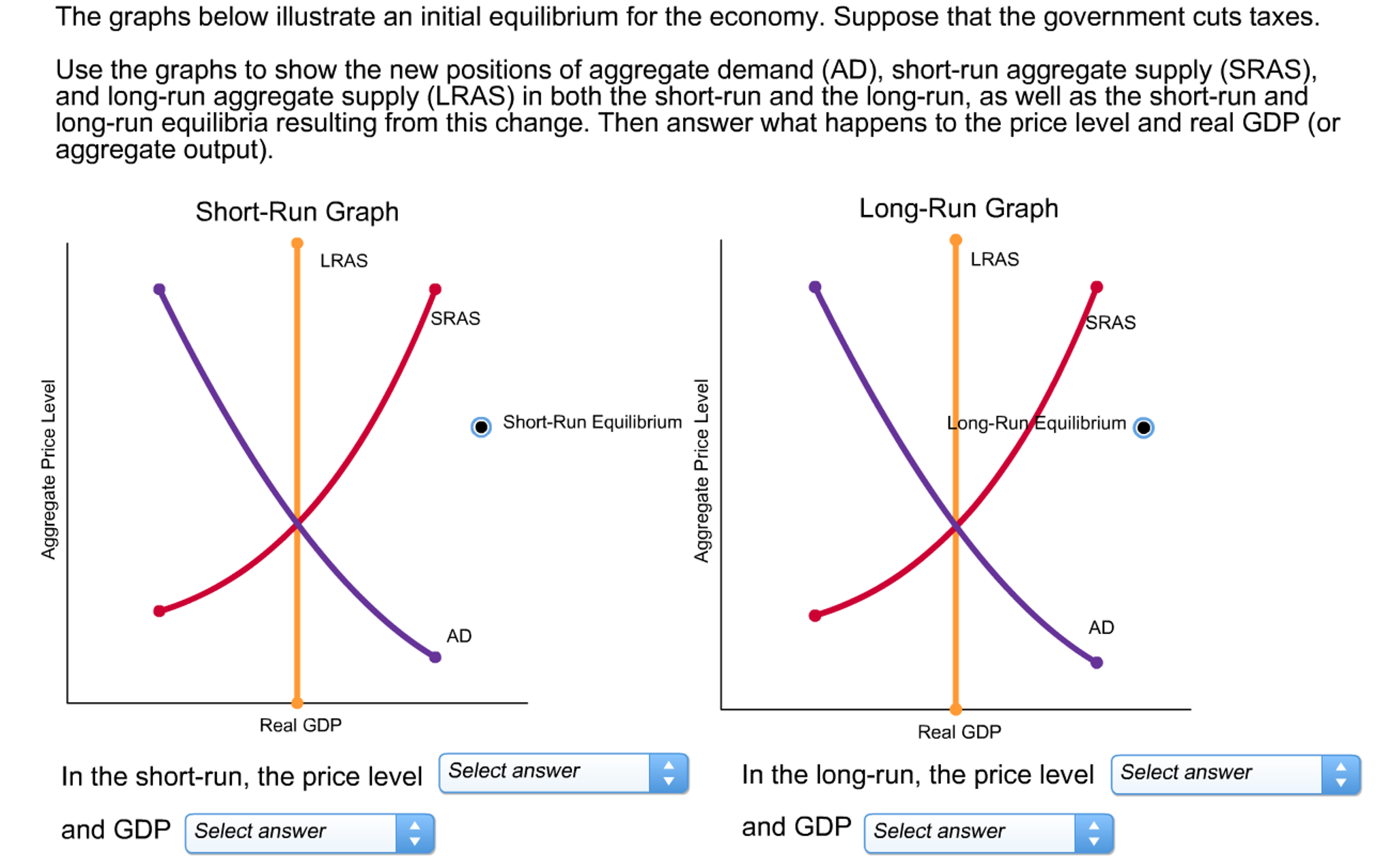
Solved The graphs below illustrate an initial equilibrium
AD-AS Model Graph. Figure 1 illustrates the AD-AS model. In this graph, notice three important curves: Aggregate demand (AD), Short-run aggregate supply (SRAS), and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS). Fig. 1 - AD-AS model graph. Aggregate demand refers to the total demand for goods and services within the economy.
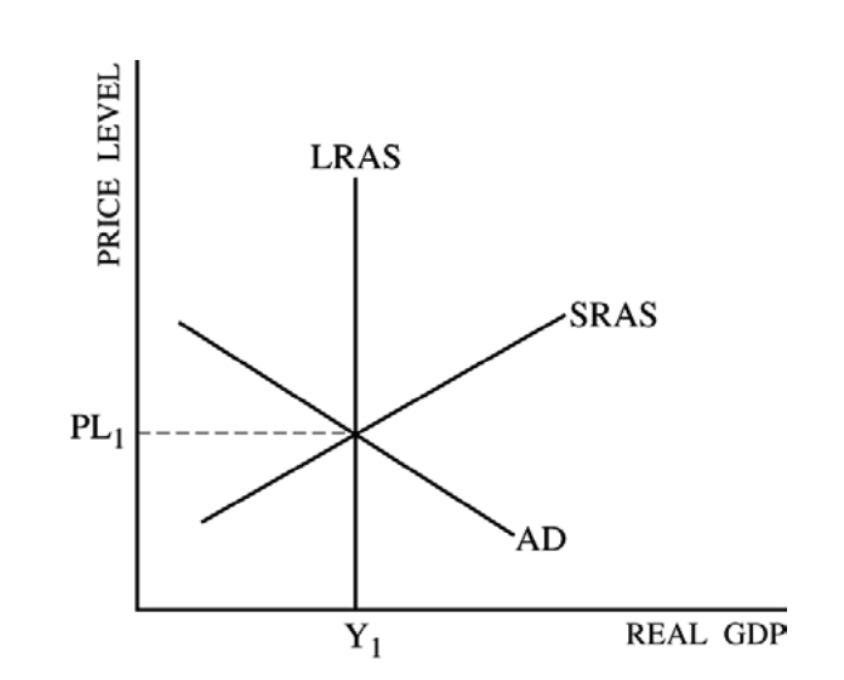
The Horizontal Axis Of A Diagram Of The Ad And As Curves Measures Which
The AD-AS or aggregate demand-aggregate supply model (also known as the aggregate supply-aggregate demand or AS-AD model) is a widely used macroeconomic model that explains short-run and long-run economic changes through the relationship of aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) in a diagram.
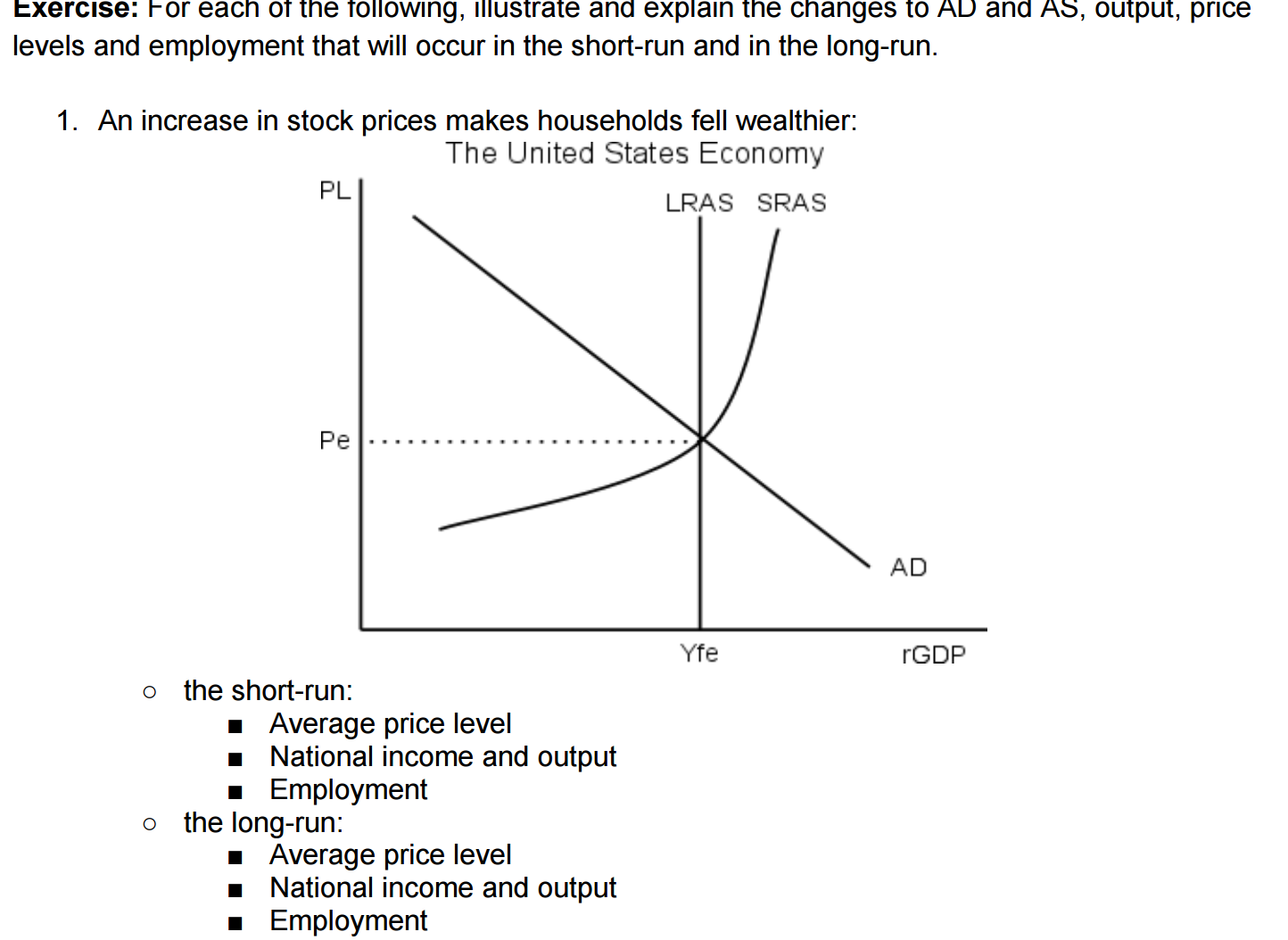
Solved Use the AD/AS model to graph and explain what happens
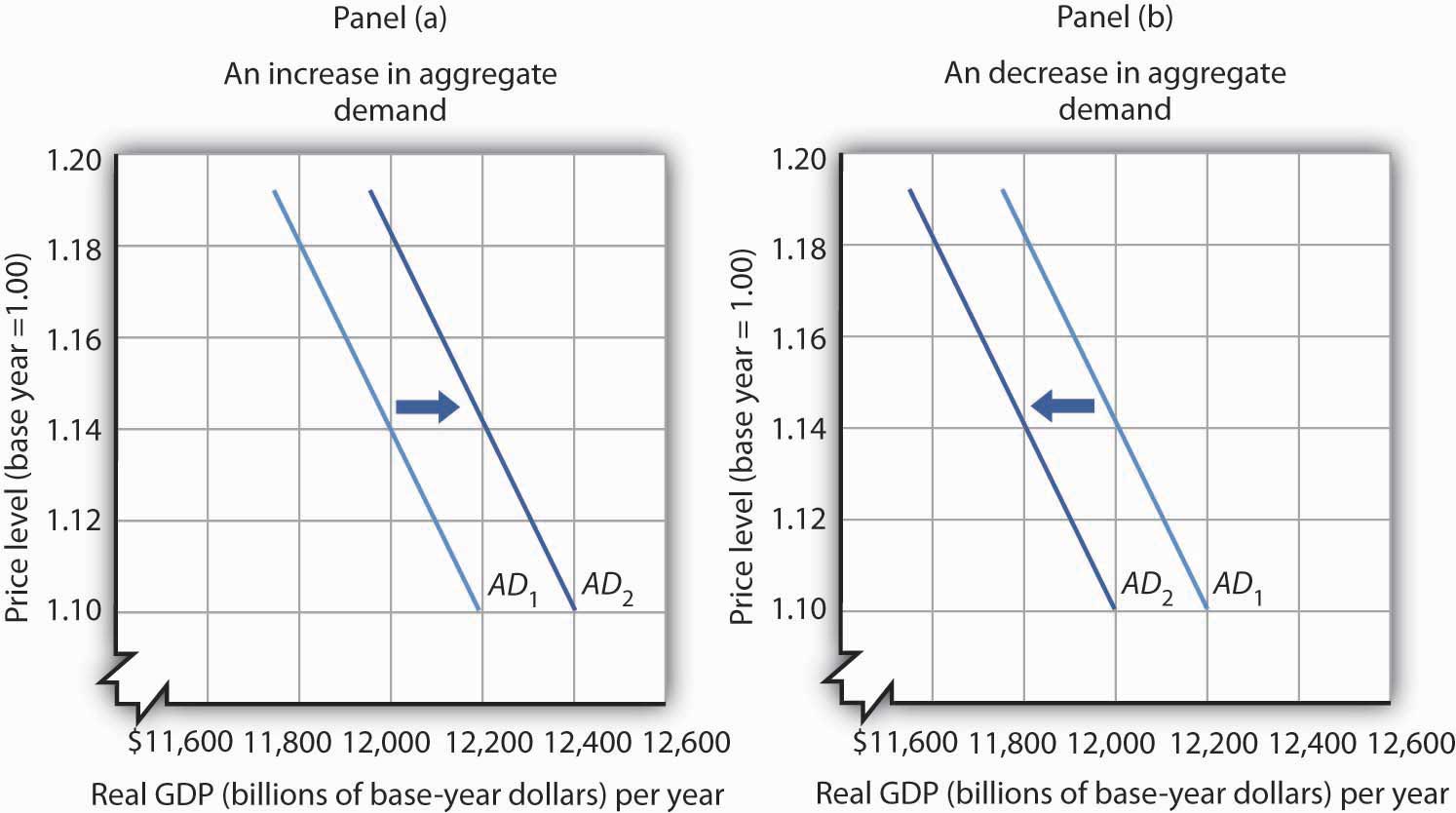
The aggregate demand curve, or AD curve, shifts to the right as the components of aggregate demand—consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and spending on exports minus imports—rise. The AD curve will shift back to the left as these components fall.

1303AFE Sem 2 ADAS Graph Example YouTube
AP Macroeconomics Study Guide. VII. AD/AS Graph. Aggregate Demand Shifters. These cause shifts in aggregate demand: C C (consumer wealth, consumer expectations, household indebtedness, taxes) I I (interest rates, expected returns on investment, business taxes, technology, degree of excess capacity) G G. Xn X n (National income abroad, exchange.
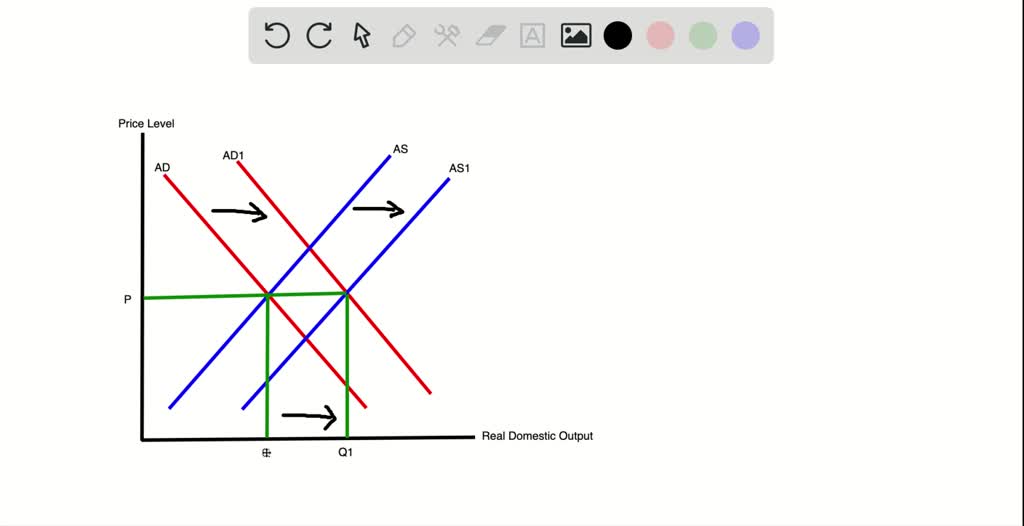
SOLVEDUse an ADAS graph to demonstrate and explain the pricelevel and
The AD curve slopes down, which means that increases in the price level of outputs lead to a lower quantity of total spending. The reasons behind this shape are related to how changes in the price level affect the different components of aggregate demand.. Plot AD on your graph. Step 3. Plot AS on your graph. Step 4. Look at Figure 24.5.
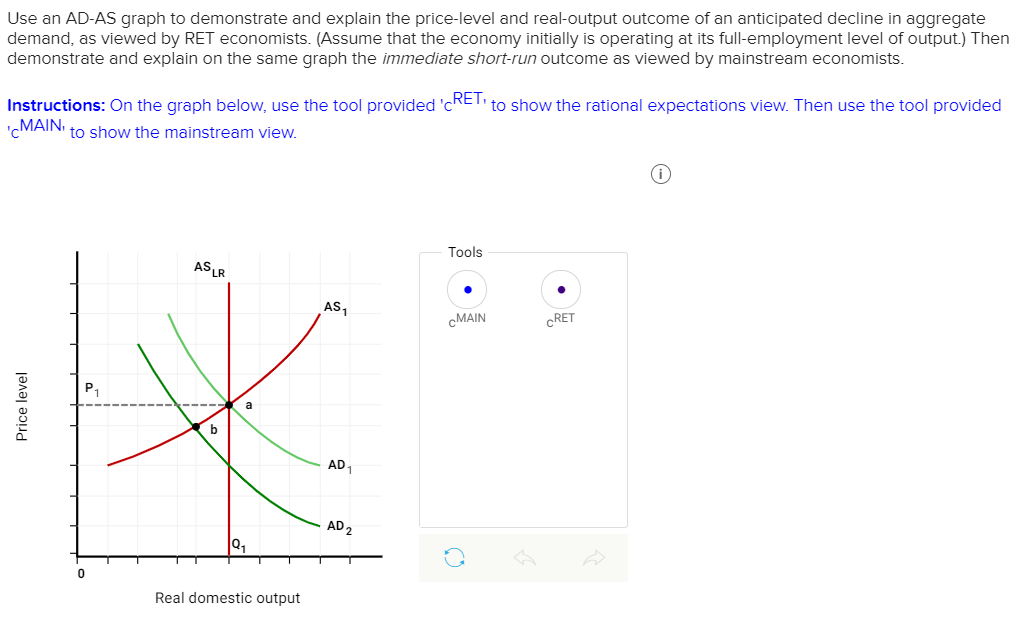
Solved Use An ADAS Graph To Demonstrate And Explain The
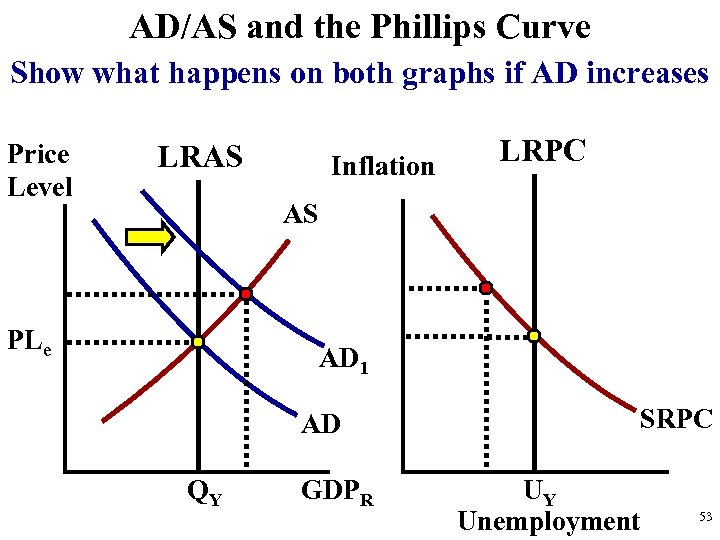
In an AD/AS diagram, long-run economic growth due to productivity increases over time is represented by a gradual rightward shift of aggregate supply. The vertical line representing potential GDP—the full-employment level of gross domestic product—gradually shifts to the right over time as well.
[Solved] PART A The Great Recession and the AD/AS Model The AD/AS
Plot AS on your graph. Step 4. Look at Figure 2, which provides a visual to aid in your analysis. Figure 2. The AS-AD Curves AD and AS curves created from the data in Table 1. Step 5. Determine where AD and AS intersect. This is the equilibrium with the price level at 130 and real GDP at $680. Step 6.
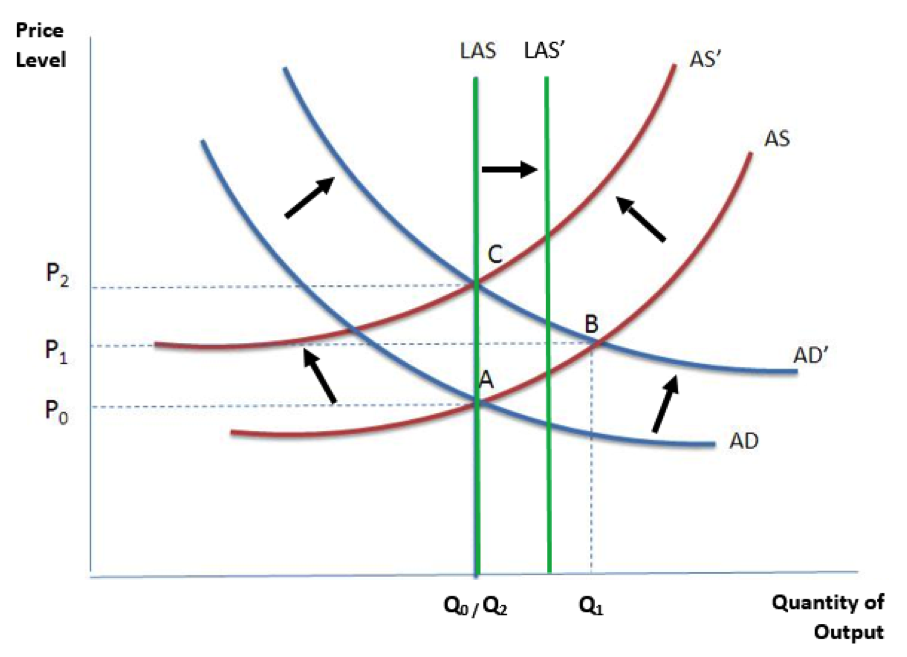
Aggregate Supply & Demand SlateRock Capital Group
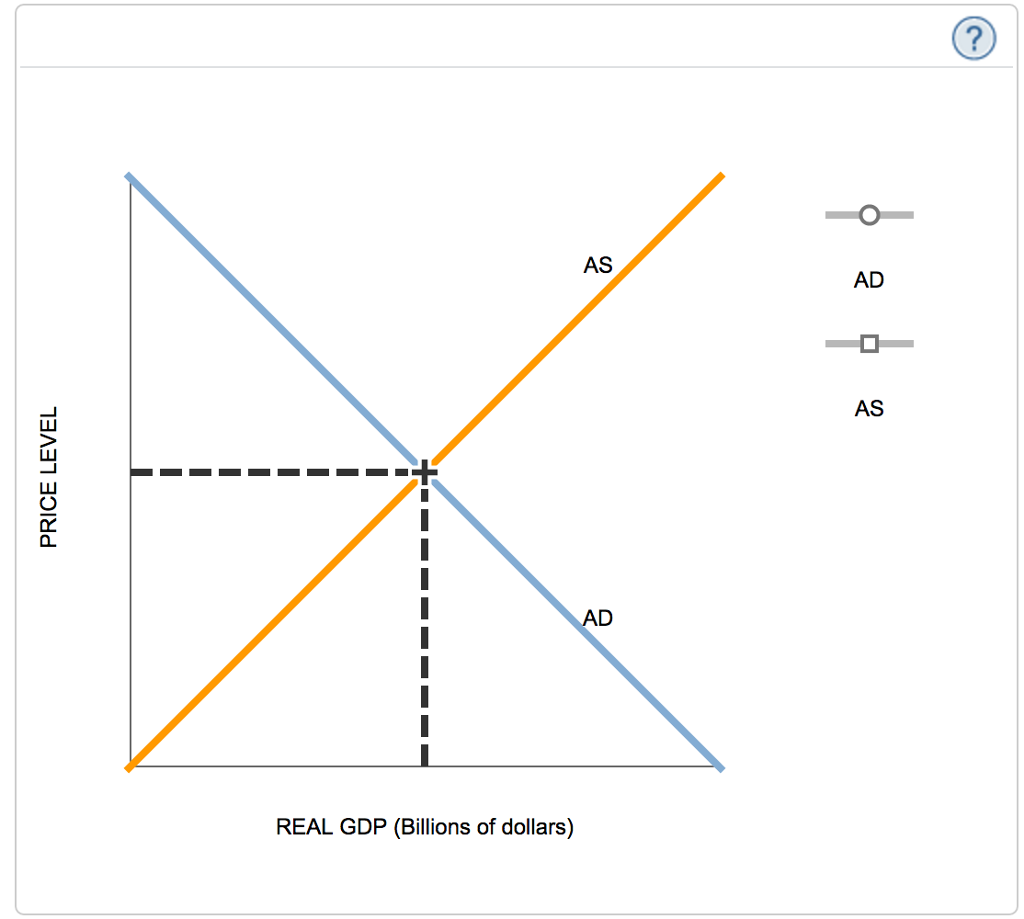
The AD-AS (aggregate demand-aggregate supply) model is a way of illustrating national income determination and changes in the price level. We can use this to illustrate phases of the business cycle and how different events can lead to changes in two of our key macroeconomic indicators: real GDP and inflation. Key Features of the AD-AS model
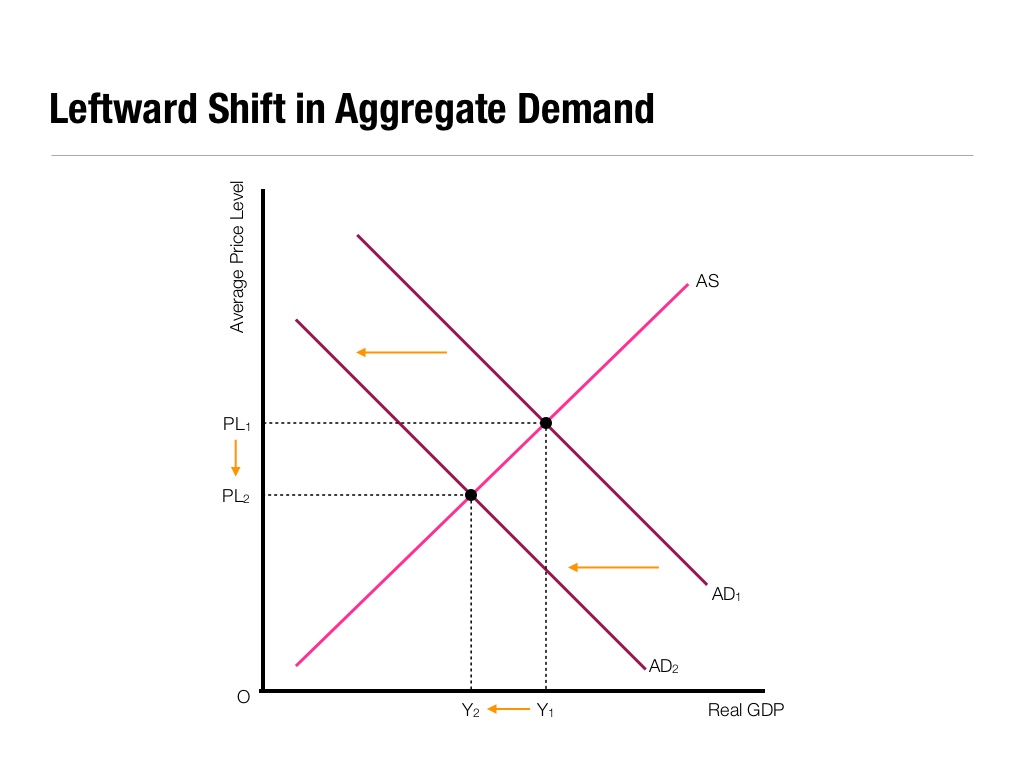
Handout An Introduction to Aggregate Demand Economic Investigations
The AD-AS Model is one of the first models that students of macroeconomics will come across. It offers a clear and simple framework for understanding how the output level in the economy (and the employment levels needed to produce that output) varies with the price level. The driving forces are, as usual, supply and demand.
[Solved] Draw a generic Aggregate Supply (AS) and Aggregate Demand (AD
We can use the AD-AS model to help explain the business cycle (in other words, the recessions and booms that we have seen in the real world). When AD or SRAS curves shift, we call these "shocks". Why a shock? Because the change come as a complete surprise!
Reading Aggregate Demand Macroeconomics
AD-AS diagram [classic] by Anjaneya Tiwari Edit this Template Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. Economics You can easily edit this template using Creately.
Unit 3 Aggregate Demand Supply and Fiscal Policy
5 May 2017 by Tejvan Pettinger Diagrams showing how shifts in aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS) affect macroeconomic equilibrium - real GDP and price level (PL) Includes short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) and classical and Keynesian view of LRAS curves.

Understanding Aggregate Demand Economics tutor2u
The AD/AS diagram shows cyclical unemployment by how close the economy is to the potential or full GDP employment level. Returning to Figure 24.9, relatively low cyclical unemployment for an economy occurs when the level of output is close to potential GDP, as in the equilibrium point E 1.
Solved Using the ADAS model to understand U.S. economic
AD-AS Model. The AD (Aggregate Demand) & AS (Aggregate Supply) model is one of the basic tools in economics as it provides general framework for bringing economic factors together in one diagram. Define aggregate demand as the total demand for an economy's output (production of goods and services) over a given period of time.